
GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft
Addressing the problem of thrombus formation on the luminal surface of a vascular graft is a challenge faced by all vascular surgeons. The GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft is specifically designed for those vascular procedures in which the risk of acute graft thrombotic failure is of clinical concern.
Patency comparable to greater saphenous vein (GSV)
Whether below-knee or above-knee, patency rates with the GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft are comparable to the gold standard of GSV.
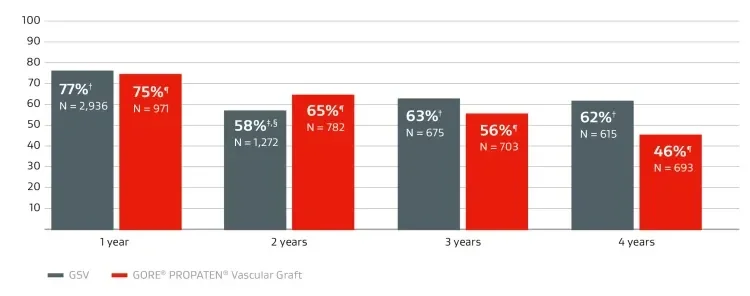
Primary patency compared to GSV
Overall weighted average* primary patency in above-knee bypasses.
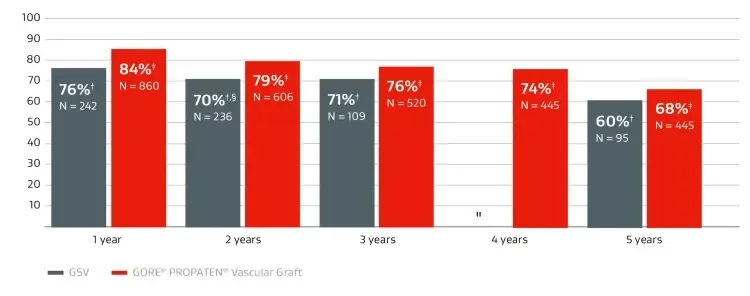
Primary patency compared to GSV
Overall weighted average* primary patency in below-knee bypasses.
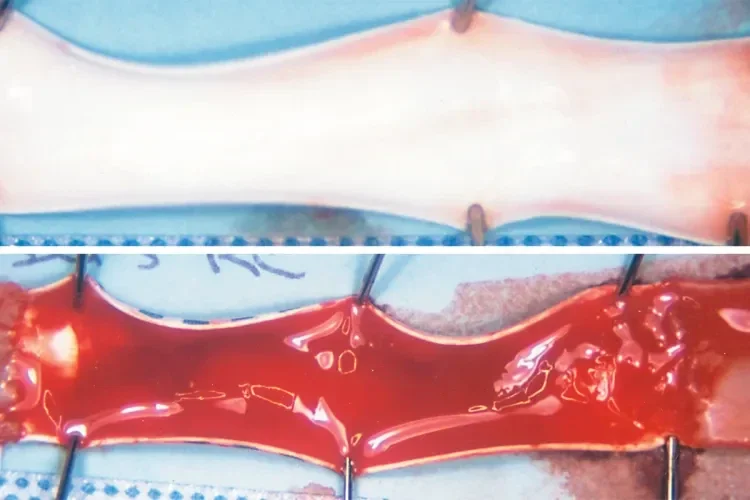
The BioActive luminal surface of a 3 mm diameter GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft (top) remains free of thrombus, while the non-bioactive surface of a control graft (below; 3 mm diameter) is covered with thrombus. Grafts were explanted after 2 hours in a challenging carotid shunt canine model.
The GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft harnesses the anticoagulant properties of heparin directly at the luminal surface of the graft. The proprietary end-point attachment mechanism, the CBAS® Heparin Surface, serves to anchor heparin molecules to the luminal surface while still maintaining heparin's intrinsic bioactive properties. The result: a thromboresistant bioactive graft surface that retains its bioactive properties.1
The GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft has demonstrated improved thromboresistance and patency compared to standard ePTFE grafts in pre-clinical in vivo tests. A randomized, multi-center clinical study has shown promising results.2 The thromboresistant surface technology employed on the GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft is designed to maintain bioactivity, thus increasing the potential for performance improvement and increased patency**.
| * Weighted Average = | (N1 × Primary Patency1) + (N2 × PP2) + … + (Nn × PPn) |
| N1 + N2 + … + Nn |
† Data based on an analysis of current literature: several MEDLINE® Database searches were performed to identify publications pertaining to ePTFE synthetic vascular graft and vein infragenicular bypasses. Search criteria included (1) articles published from January 2000 to January 2012, (2) key words used were below knee, polytetrafluoroethylene, prosthetic, bypass, patency, (3) articles in English language, (4) N equal or greater than 30 bypasses, (5) clinical publications, (6) reviews, case reports or meta-analysis articles were excluded, (7) articles containing the keyword AV access (including synonyms) were excluded. Articles that did not meet the above criteria were deemed ineligible for this analysis (data on file 2019; W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc; Flagstaff, AZ.).
‡ Above-knee (AK) inclusion criteria for GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft literature used in this analysis were (1) articles in English language, (2) clinical journal articles or book chapters, (3) non-overlapping patient populations and (4) AK bypass primary patency reported for at least 12 months of follow-up. Additional exclusion criteria were (1) reviews, case reports or meta-analysis articles and (2) articles containing the key word AV access (including synonyms) (data on file 2019; W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc; Flagstaff, AZ.).
§ In studies where one-year and three-year patency data were reported, but two-year patency data were not reported, the two-year patency rate used in this analysis was interpolated as the average of the one-year and three-year patency rates.
ǁ Data not reported.
¶ Below-knee (BK) inclusion criteria for GORE® PROPATEN® Vascular Graft literature used in this analysis were (1) articles in English language, (2) clinical journal articles or book chapters, (3) non-overlapping patient populations, (4) BK bypass primary patency reported for at least 12 months of follow-up and (5) N = 50 or more BK bypasses. Additional exclusion criteria were (1) reviews, case reports or meta-analysis articles and (2) articles containing the key word AV access (including synonyms) (data on file 2019; W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc; Flagstaff, AZ.).
** Long-term data are not available regarding improved patency compared to market grafts.
- Begovac PC, Thomson RC, Fisher JL, Hughson A, Gällhagen A. Improvements in GORE-TEX® Vascular Graft performance by Carmeda® bioactive surface heparin immobilization. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery 2003;25(5):432-437.
- Lindholt JS, Gottschalksen B, Johannesen N, et al. The Scandinavian Propaten® Trial – 1-year patency of PTFE vascular prostheses with heparin-bonded luminal surfaces compared to ordinary pure PTFE vascular prostheses – a randomised clinical controlled multi-centre trial. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery 2011;41(5):668-673.
Featured resources
22777242-EN
