GORE® VIABAHN® Device family
Treatment Options
Join the next generation of care in the treatment of aortoiliac occlusive disease
Covered stents: Key advantages for complex lesions
Covered stents help address the shortcomings of bare metal stents1-3 in treating complex aortoiliac occlusive disease (AIOD) by:
- Excluding plaque.
- Preventing in-stent neointimal hyperplasia.2-4
- Decreasing the risk of complications caused by distal embolization, perforation, rupture and dissection.5,6
- Covering and sealing off vessel ruptures.
- Promoting hemodynamic flow via a new flow lumen.
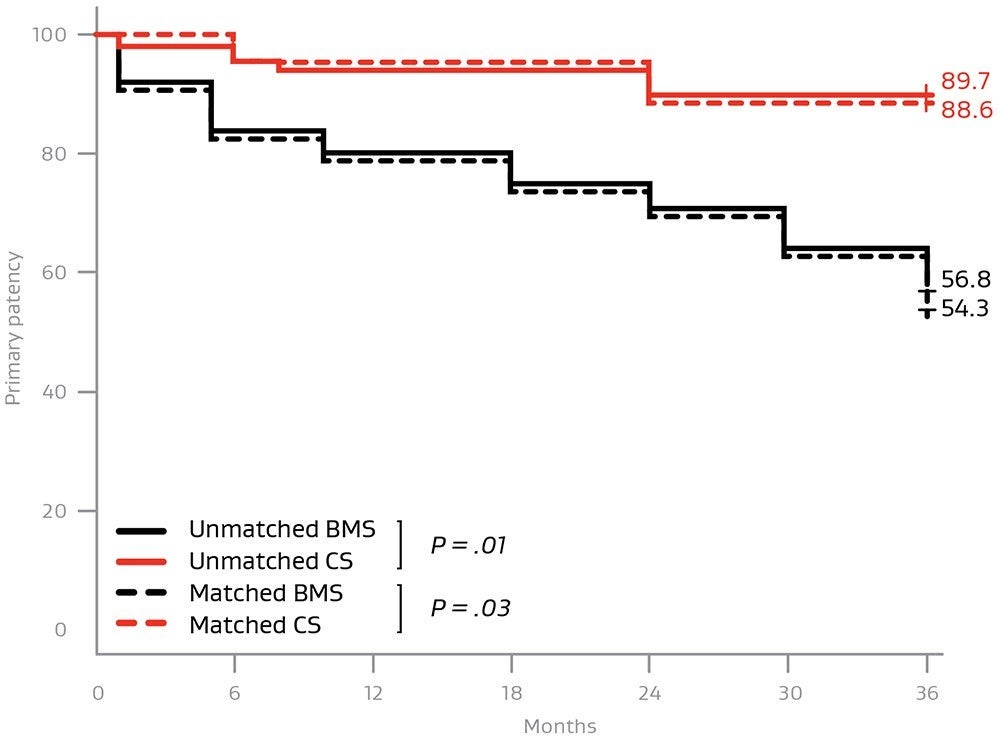
Covered stent grafts have shown excellent outcomes for treating complex AIOD

Covered stents are providing higher midterm patency rates compared to bare metal stents for:
- TASC D lesions
- Iliac occlusions with a total lesion length > 6 cm
- Occlusion length > 3.5 cm
- Calcification involving > 75% of the arterial wall circumference
Additional patient benefits versus baseline
A systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials and four retrospective cohort studies compared outcomes with covered and uncovered stents when treating AIOD.8
The covered stent group demonstrated:
+ .08 higher
ankle-brachial index
(Mean difference: .08, 95% CI .07 to .09, P < .001)
81% lower
odds of reintervention
(Odds ratio: .19, 95% CI .09 to .42, P < .001)
Self Expanding or Balloon Expandable – when to use:
SELF-EXPANDING STENT (SX)
- Shape memory alloys (e.g., nitinol).
- Deployed via release of constraining mechanism.
BALLOON-EXPANDING STENT (BX)
- Ductile metal alloys (e.g., stainless steel).
- Deployed via angioplasty balloon inflation.
Attribute | |
|---|---|
| Radial strength / recoil resistance | BX > SX |
| Diameter adjustment (taper / flare) | BX > SX |
| Deployment accuracy | BX > SX |
| Compression recovery | SX > BX |
| Trackability / implanted conformability | SX > BX |
| Length of device | SX > BX |
| Device profile | BX > SX |
*As used by Gore, PROPATEN Bioactive Surface refers to Gore’s proprietary CBAS® Heparin Surface.
- Piazza M, Squizzato F, Dall'Antonia A, et al. Outcomes of self expanding PTFE covered stent versus bare metal stent for chronic iliac artery occlusion in matched cohorts using propensity score modelling. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery 2017;54(2):177-185.
- Mwipatayi BP, Sharma S, Daneshmand A, et al; COBEST co-investigators. Durability of the balloon-expandable covered versus bare-metal stents in the Covered versus Balloon Expandable Stent Trial (COBEST) for the treatment of aortoiliac occlusive disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2016;64(1):83-94.e1.
- Sabri SS, Choudhri A, Orgera G, et al. Outcomes of covered kissing stent placement compared with bare metal stent placement in the treatment of atherosclerotic occlusive disease at the aortic bifurcation. Journal of Vascular & Interventional Radiology 2010;21(7):995-1003.
- Bismuth J, Gray BH, Holden A, Metzger C, Panneton J; VBX FLEX Study Investigators. Pivotal study of a next-generation balloon-expandable stent-graft for treatment of iliac occlusive disease. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2017;24(5):629-637.
- Squizzato F, Piazza M, Pulli R, et al; ILIACS Registry Group. Covered versus bare metal kissing stents for reconstruction of the aortic bifurcation in the ILIACS registry. Journal of Vascular Surgery. In press.
- Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Guidelines Writing Group, Conte MS, Pomposelli FB, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines for atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the lower extremities: management of asymptomatic disease and claudication. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2015;61(3) Supplement:2S-41S.
- Laird JR, Zeller T, Holden A, et al; BOLSTER Investigators. Balloon-expandable vascular covered stent in the treatment of iliac artery occlusive disease: 9-month results from the BOLSTER Multicenter Study. Journal of Vascular & Interventional Radiology 2019;30(6):836-844.e1.
- Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Antoniou SA, Torella F, Antoniou GA. Covered vs uncovered stents for aortoiliac and femoropopliteal arterial disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2016;23(3):442-452.

Refer to Instructions for Use at eifu.goremedical.com for a complete description of all applicable indications, warnings, precautions and contraindications for the markets where this product is available. RXonly
GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with PROPATEN Bioactive Surface
INDICATIONS FOR USE IN EUROPE: The GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with PROPATEN Bioactive Surface is indicated for the treatment of:
- de novo or restenotic lesions in the iliac arteries
- de novo or restenotic lesions in the superficial femoral artery and proximal popliteal artery
- in-stent restenotic lesions in the superficial femoral artery and proximal popliteal artery
- stenosis or thrombotic occlusion at the venous anastomosis of synthetic arteriovenous (AV) access grafts and in the venous outflow of dialysis access circuits, including the central veins
- popliteal artery aneurysms and isolated visceral artery aneurysms
- traumatic or iatrogenic vessel injuries in arteries that are located in the chest cavity, abdominal cavity, or pelvis (except for aorta, coronary, innominate, carotid, vertebral, and pulmonary arteries)
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Non-compliant lesions where full expansion of an angioplasty balloon catheter was not achieved during pre-dilatation, or where lesions cannot be dilated sufficiently to allow passage of the delivery system.
- Do not use the GORE® VIABAHN® Endoprosthesis with PROPATEN Bioactive Surface in patients with known hypersensitivity to heparin, including those patients who have had a previous incident of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) type II.
GORE® VIABAHN® VBX Balloon Expandable Endoprosthesis
INDICATIONS FOR USE IN EUROPE: The GORE® VIABAHN® VBX Balloon Expandable Endoprosthesis is indicated for the treatment of:
- de novo or restenotic lesions found in iliac arteries, including lesions at the aortic bifurcation;
- de novo or restenotic lesions in the visceral arteries;
- isolated visceral, iliac, and subclavian artery aneurysms; or
- traumatic or iatrogenic vessel injuries in arteries that are located in the chest cavity, abdominal cavity, or pelvis (except for aorta, coronary, innominate, carotid, vertebral, and pulmonary arteries).
The GORE® VIABAHN® VBX Balloon Expandable Endoprosthesis is indicated for use as a bridging stent in branched and fenestrated endovascular aortic aneurysm repair with the following*:
- Approved for use branched aortic endovascular grafts constructed of polyester fabric, stainless steel stents, and polypropylene suture with branch diameters of 6/8 mm and lengths of 18/21 mm.
- Approved for use fenestrated aortic endovascular grafts constructed of polyester fabric, stainless steel stents, and fenestrations with polypropylene suture ranging in diameter from 6–8 mm.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use the GORE® VIABAHN® VBX Balloon Expandable Endoprosthesis in patients with known hypersensitivity to heparin, including those patients who have had a previous incident of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) type II.
*Not applicable to Reduced Profile GORE® VIABAHN® VBX Balloon Expandable Endoprosthesis (BXB catalogue numbers).